

Projectile motion is a form of motion experienced by an object or particle that is thrown near the Earth's surface and moves along a curved path under the action of gravity only (in particular, the effects of air resistance are assumed to be negligible). There are many types of motion around us. Football, baseball, cricket ball, and any other object are instances of projectile motion. Don't forget to consider the direction of motion when analyzing the problem!The path that an object takes when thrown at an angle other than 90 degrees from a horizontal point is known as a trajectory, the object is known as a projectile, and the motion is defined as the projectile motion.Use the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus to relate the velocity function to the position function.Use integration to find displacement and average velocity, given a velocity function.Remember that displacement is the change in position, and average velocity is the total displacement divided by the time interval.Use the equations of motion (such as x(t) = x0 + v0t + 1/2at^2) to find position, velocity, or acceleration at any time, given initial conditions.Use the velocity-time graph to find the acceleration at any point in time.Use the slope of the position-time graph to find the velocity at any point in time.Use position-time graphs to visualize the motion and make it easier to understand the problem.Here are some tips for using calculus to analyze 2D kinematics problems: You can also see why AP says that you can assume "air resistance is negligible." 😅 You might be confused on how projectile motion still works, so try out the PhET Simulation below to experiment with different factors of projectile motion (i.e., time, velocity, acceleration)! The range of the projectile (the horizontal distance it travels) can be found by setting the y coordinate of the projectile to 0 and solving for the time t.We can also use calculus to find the maximum height reached by the projectile and the time it takes for the projectile to reach this maximum height.Using calculus, we can find the velocity and acceleration of the projectile at any time t by taking the first and second derivatives of the position equations.

This means that the velocity of the projectile in the y direction (vy) is constantly changing at a rate of -g.

The path that the projectile follows is called its trajectory.Projectile motion refers to the motion of an object that is projected into the air and then is subject to the force of gravity. This is where projectile motion usually comes in.
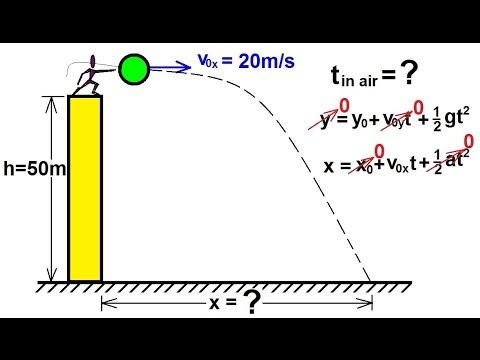
2D PROJECTILE MOTION EQUATIONS HOW TO
Great! You know how to consider motion in 1 dimension! Is your brain ready to handle TWO dimensions?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
